
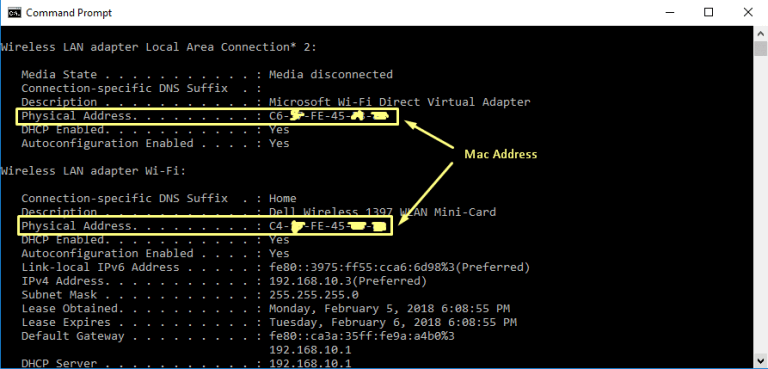
At the hardware level of your network card, though, your network card is only looking at other MAC addresses for interfaces on the same network. Your computer sends the request to your router, which then sends it out onto the Internet.
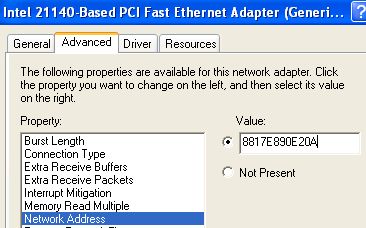
The web address you type gets translated to the IP address of the server. When a browser on your computer needs to grab a web page from a server on the Internet, for example, that request passes down through several layers of the TCP/IP protocol. What MAC Addresses Are Used ForĪt the lowest networking level, network interfaces attached to a network use MAC addresses to communicate with one another. These MAC addresses-sometimes referred to as physical or hardware addresses-are assigned in the factory, but you can usually change the addresses in software.
MAC Filtering : Limits the no of MAC addresses to a certain extent.Each network interface connected to your network-whether it’s your router, wireless device, or network card in your computer-has a unique media access control (MAC) address. Implementation of 802.1X : Allows packet filtering rules issued by a centralised AAA server based on dynamic learning of clients. Port Security : Limits the no of MAC addresses connecting to a single port on the Switch. Some of the major countermeasures against MAC Flooding are: Such kind of layer 2 stress testing can be done with this handy tool. Some switches tend to crash & reboot also. Some switches behave like hubs, transmitting all source packets to all destinations. This tool can be used in such situations to check if the switch is overloaded. Some switches don’t allow to spoof arp packets. While conducting a pentest, this tool comes in handy while sniffing. command: macof -i eth1 -d 192.168.1.1 Targeted Flooding Macof can flood a switch with random MAC addresses destinated to 192.168.1.1. command: macof -i eth1 -n 10 Random Flooding LAB 2: Targeted Flooding This fills in the switch’s CAM table, thus new MAC addresses can not be saved, and the switch starts to send all packets to all ports, so it starts to act as a hub, and thus we can monitor all traffic passing through it. Macof can flood a switch with random MAC addresses. n times Specify the number of packets to send. Homepage Options Syntax: macof -i interface Specify the interface to send on. While this is nice for a hacker, most networks use switches, which inherently restrict this activity. This allows that device to simply collect all the data passing through a hubbed network. However, in a hubbed network, sniffing data is very easy to accomplish by placing a network card into promiscuous mode. 
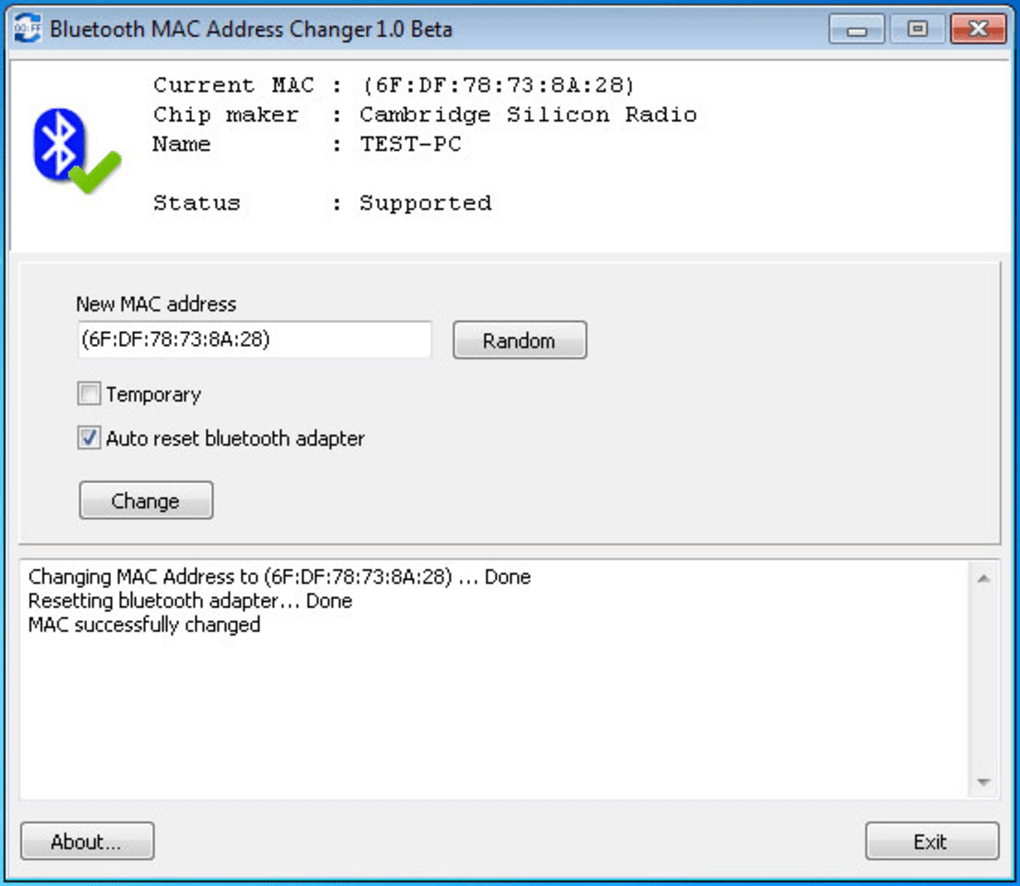
The data is typically rejected by all network cards, except the one it was intended for. A passive hub has no mapping, and thus broadcasts line data to every port on the device. This is the main difference between a switch and passive hub. It actively monitors (cache) the MAC address on each port, which helps it pass data only to its intended target. The reason for this is that the switch regulates the flow of data between its ports. Macof is a member of the Dsniff suit toolset and mainly used to flood the switch on a local network with MAC addresses.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
